Thursday, December 4, 2008
Install Java in Fedora
Download the java package and install it.
cd /usr/lib/mozilla/plugins
ln -s /usr/java/jre1.6.0_11/plugin/i386/ns7/libjavaplugin_oji.so
DirectoryName or FileName with a space at end
Cannot delete files or directories when there are spaces at end of the name.
C:\test>dir

 C:\test>del "file://?/c:/test/my.txt "
C:\test>del "file://?/c:/test/my.txt "C:\test>

Tuesday, November 11, 2008
SideBySide
Resolve Partial Assembly failed for Microsoft.VC80.MFCLOC. Reference error message: The referenced assembly is not installed on your system.
Generate Activation Context failed for C:\WINDOWS\WinSxS\x86_Microsoft.VC80.MFC_1fc8b3b9a1e18e3b_8.0.50727.762_x-ww_3BF8FA05\MFC80.DLL. Reference error message: The referenced assembly is not installed on your system.

Tuesday, October 28, 2008
win32time error

Firewall configuration:
New Traffic policy:
 Source: Any
Source: Any
Destination: Time.Windows.Com
Service: NTP
Action: permit
Translation: NAT
PDC Emulator Role:
Net Time /setsntp:time.windows.com
DC:
Net time /setsntp:PDC Server
Member:
Net time /setsntp:PDC Server
After the configuration, in event viewer, you will see:
PDC Server: Zeeman2.vanarts.com
The time provider NtpClient is currently receiving valid time data from time.windows.com (ntp.m0x0191.121.11.2:123->207.46.197.32:123).
The time service is now synchronizing the system time with the time source time.windows.com (ntp.m0x0191.121.11.2:123->207.46.197.32:123).
Member server:
The time provider NtpClient is currently receiving valid time data from zeeman2 (ntp.m0x0191.121.11.1:123->191.121.11.2:123).
The time service is now synchronizing the system time with the time source zeeman2 (ntp.m0x0191.121.11.1:123->191.121.11.2:123).
Monday, October 27, 2008
Saturday, October 25, 2008
DSACLS.exe to restore permissions for Default global address list
You must have the Windows Support Tools installed.
ADSIEDIT.MSC console
Deny READ Permission for Authenticated Users.


You cannot modify the permissions of Default Global Address List.
You cannot create new outlook profiles.
C:\Program Files\Support Tools>dsacls.exe "CN=Default Global Address List,CN=All Global Address Lists,CN=Address Lists Container,CN=Workopera,CN=Microsoft Exchange,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=work,DC=com" /R "Authenticated Users"
C:\Program Files\Support Tools>dsacls.exe "CN=Default Global Address List,CN=All Global Address Lists,CN=Address Lists Container,CN=Workopera,CN=Microsoft Exchange,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=work,DC=com" /I:T
Sunday, October 19, 2008
Task "Microsoft Exchange server' reported error (0x8004010F): 'The operation failed. An object could not be found'

On EX20071 exchange 2007 server, create a new offline address list:




Friday, October 10, 2008
Windows Internal Database (Microsoft##SSEE)
np:\\.\pipe\MSSQL$MICROSOFT##SSEE\sql\query
Saturday, September 20, 2008
Exchange2007:Safe Recipients
In outlook 2003 or later, I understand the Safe Senders list without problem. However, I puzzle at Safe Recipients List.
One thing is for sure, which is you should not put your own e-mail address under the Safe Recipients list. If you do, all mail including junk mail goes to your inbox.
Another thing is for you to understand the distribution group or distribution list. If you are the member of SeniorGroup distribution list with e-mail address SeniorGroup@terrace.com, a message sent to SeniorGroup@terrace.com will be delivered to your inbox if you put SeniorGroup@terrace.com under Safe Recipients List.
From: BaseShaw1 <BaseShaw1@terrace.com>To: Senior Group <SeniorGroup@terrace.com>Date: Sat, 20 Sep 2008 17:06:39 -0700Subject: test
Within your own organization, you don't need to put the Distribution List under Safe Recipients List. If you are a member of distribution list of Internet domain and you want to receive e-mail delivered to this group, you're better to put the distribution group e-mail address in Safe Recipients List.
Wednesday, September 10, 2008
Cisco router 1811: Port forwarding with NAT





Cisco router 1811: NAT configuration
Saturday, August 30, 2008
Exchange:Import customized Contacts Item folder
Outlook was set up with POP3 account. My Contacts have Contacts and Test Contacts 2008 folders.
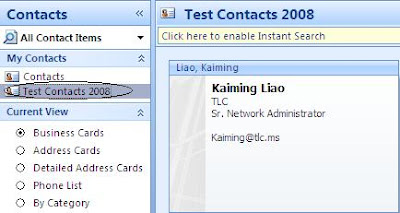
Export the whole personal folder to a pst file;
Create a new outlook profile with Exchange Server setup;
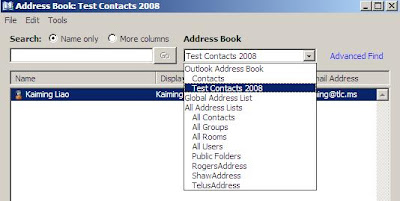
After importing the pst file to the Exchange server profile, the Test Contacts 2008 folder shows when you click Contacts in Outlook. But the Test Contacts 2008 does not show in Address Book:
 What do you do?
What do you do?
Create a Contacts Items folder with the same name and put it in MAILBOX folder (not contacts folder) as shown below:

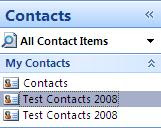
Drag and drop all Contacts from old "Test Contacts 2008" to the newly-created Test Contacts 2008" folder;
Remove the old "Test Contacts 2008" folder;
You would have the same address book structure as POP3 account profile.
Friday, August 8, 2008
Exchange2007:Export-Mailbox -DeleteContent
A virus message was delivered to all mailboxes in server1. The subject is "I Love You!"
How can you delete it from the Exchange management shell?
get-mailbox -Server tlc25 I Add-MailboxPermission -AccessRights 'FullAccess' -User Administrator -confirm $false
New-Mailbox -Name 'Temp1' -Alias 'Temp1' -UserPrincipalName 'Temp2@TLCTest.local' -SamAccountName 'Temp1' -FirstName 'Temp1' -LastName '' -Database 'TLC25\First Storage Group\Mailbox Database'
get-mailbox -Server Tlc25 I Export-Mailbox -includefolders \inbox -SubjectKeywords 'I love you!' -TargetMailbox temp1 -TargetFolder virus -DeleteContent -confirm:$false
get-mailbox -Server tlc25 I Remove-MailboxPermission -AccessRights 'FullAccess' -User Administrator -confirm $false
======
DeleteContent
---delete the content from the source mailbox after it has been exported to a folder. The source folder will not be deleted.
Exchange2007:RemoteDomain and OOF (Out-of-Office)
For most, we must understand "An Out-of-Office message is set on the clients (Outlook and OWA) but is sent by Exchange server."
How many types of clients do we have?
Outlook 2007
Outlook 2003 or earlier
OWA 2007
OWA 2003 or earlier

In Exchange Management Console, the remote domain property has the following settings:
- Allow none ----I know it means no OOF sends to remote domain.
- Allow external out-of-office messages only ----???
- All external out-of-office messages and out-of-office messages set by Outlook 2003 or earlier clients or sent by Exchange server 2003 or earlier servers ----???
- Allow internal out-of-messages, and out-of-office messages set by outlook 2003 or earlier clients or sent by Exchange server 2003 or earlier servers ----???
"Allow external out-of-office messages only" allows the external OOF messages from Outlook 2007 and OWA 2007.
"All external out-of-office messages and out-of-office messages set by Outlook 2003 or earlier clients or sent by Exchange server 2003 or earlier servers" allows the external OOF messages from Outlook 2007 and OWA 2007, and OOF messages from Outlook 2003 and OWA 2003 or earlier. Outlook 2003 and OWA 2003 don't have the external OOF and internal OOF feature.
"Allow internal out-of-messages, and out-of-office messages set by outlook 2003 or earlier clients or sent by Exchange server 2003 or earlier servers" allows the internal OOF messages from Outlook 2007 and OWA 2007, and OOF messages from Outlook 2003 and OWA 2003 or earlier.
The following cmdlet controls the individual mailbox can only send internal OOF messages.
SET-MAILBOX -IDENTITY 'Kevin.Smith' -ExternalOofOptions InternalOnly
Wednesday, August 6, 2008
Exchange2007:Hub Site
Least cost path
Site A to Site D has two paths.
Site A+Site B+Site D (cost=5+15)
Site A+Site C+Site D (cost=5+5)
The path A+C+D is chosen.
 How do you understand the direct delivery?
How do you understand the direct delivery?After the least cost path is selected, Hub transport server in Site A will directly deliver messages to the Hub Transport server in Site D. The Hub Transport server in Site C does not process the messages at all.
If you want the HUB Transport Server in SITE C to process the message, configure it as a hub site.
Set-AdSite -identity "Site C' -HubSiteEnabled:$true
Why would you do that?
One example will be that a company implements the centralized journaling.
Most of the time, you should not define a HUB Site. For this scenario, if Hub transport server in SITE C does not work, because Site C is a hub site, the messages from SITE A cannot be delivered to Site D.
If Site C is not defined as a HUB SITE, mail is directly delivered from SITE A to SITE D. Direct relay is not affected by lack of network connectivity between SITE A and Site C.
Exchange2007:3-way that messages go into the Transport Server
Exchange2007:RBL configuration
Match to specific mask and responses.
 What is the mask? What is the response?
What is the mask? What is the response?Examples of return status code:
127.0.0.1 – Blocklist
127.0.0.2 – Known Open Relay
127.0.0.4 – DialUp IP Address
Mask for matching:
Binary for last byte of IP version 4
0000 0001 – Blocklist --127.0.0.1,127.1.0.1,etc.
0000 0010 – Open Relay --127.0.0.2, 127.1.0.2, etc
0000 0011 – Open relay or Blocklist --127.0.0.1,127.0.0.2,127.1.0.1,127.1.0.2, etc
0000 0100 – Dialup host --127.0.0.4,127.1.0.4,etc
0000 0101 – Dialup or Blocklist --127.0.0.1,127.0.0.4,127.1.0.1,127.1.0.4,etc
0000 0110 – Dialup or Openrelay
0000 0111 – Dialup, Openrelay, or Blocklist
Get-IPBlockListProvider example3 [pipe line] fl bitmaskMatch,IPAddressesMatch
BitmaskMatch : 0.0.0.2
IPAddressesMatch : {127.0.0.5, 127.0.0.4, 127.0.0.3}
Exchange2007:Message Size Limit
Organization Level
Get-TransportConfig fl max*
MaxDumpsterSizePerStorageGroup : 18MB
MaxDumpsterTime: 7.00:00:00
MaxReceiveSize: 10MB
MaxRecipientEnvelopeLimit : 5000
MaxSendSize : 10MB
Mailboxes: Simon and Tam
('simon','tam') get-mailbox fl name,max*
Name : simon
MaxSafeSenders :
MaxBlockedSenders :
MaxSendSize : unlimited
MaxReceiveSize : unlimited
Name : TAM
MaxSafeSenders :
MaxBlockedSenders :
MaxSendSize : unlimited
MaxReceiveSize : unlimited
Simon cannot send a message to TAM with an attachment over 10MB.
('simon','tam') set-mailbox -MaxSendSize 80MB
('simon','tam') set-mailbox -MaxReceiveSize 80MB
Simon can send a message to TAM with an attachment size of 20MB, even though the Organizational Message Size limit is still 10MB.
Within the same site, there is no Maximum Message Size limit defined. By setting up limit on individual maibox, you create the exception to Organizational Limit of Maximum Message Size.
---------
By default, Exchange 2007 does not impose a maximum message size limit on messages that are relayed between Hub Transport servers in different Active Directory sites or across routing group connectors to Legacy Exchange servers.
Set-AdSiteLink -Identity DEFAULTIPSITELINK -MaxMessageSize 10MB
Sunday, August 3, 2008
Exchange2007:one certificate for multiple domain names
ways to access web server:
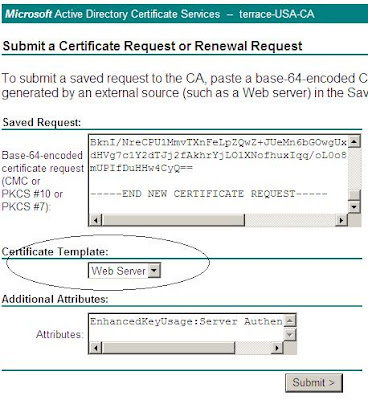
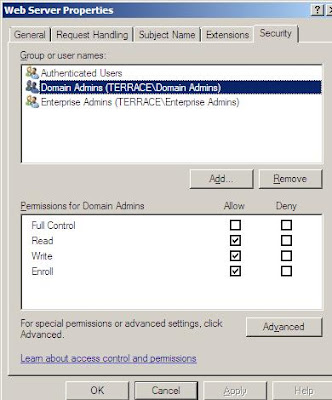
By default, only domain admins and enterprise admins have the Enrol permission.
Download the certificate to c:\certnew.cer
Import-ExchangeCertificate -path C:\certnew.cer
Find the thumbprint of the certificate:
Get-exchangeCertificate USA
Enable-ExchangeCertificate -Services smtp,iis -Thurmprint
Friday, August 1, 2008
Exchange2007:Free/Busy-Availability-Calendar
Free/Busy --availability
Clients: Microsoft Outlook client,Outlook Web Access and Outlook Mobile Access
It refers to the Calendar folder of a mailbox.
The free/busy data is used extensively when scheduling meetings.
Outlook 2003 client
The Free/busy data is stored as messages in a dedicated system public folder. Each administrative group in the Exchange organization includes a Free/Busy folder.
Outlook 2007 client
When Exchange 2007 services OUTLOOK 2007, it does not use the public folder for OAB and free/busy data. Autodiscover service is automatically installed when Client Access Role is installed. The Autodiscover service helps Outlook 2007 locate various Web services, such as the Unified Messaging, Offline Address Book, and Availability services.
WHEN Outlook 2007 is configured with exchange 2003 mailbox user, it uses the public folder for OAB and free/busy data.
If you are providing external access to Microsoft Exchange by using Outlook Anywhere (formerly known as RPC over HTTP), and you want your Outlook 2007 clients to be automatically configured by using the Autodiscover service, you must install a valid Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate on the Client Access server that includes both the common name (for example, mail.contoso.com) and a Subject Alternative Name for autodiscover.contoso.com.
Access Autodiscover service from Internet
Set-WebServicesVirtualDirectory -identity "CAS01\EWS (Default Web Site)" -externalurl https://mail.contoso.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx -BasicAuthentication:$True
Access Offline Access Book from Internet
Set-OABVirtualDirectory -identity "CAS01\OAB (Default Web Site)" -externalurl https://mail.contoso.com/OAB -RequireSSL:$true
Test-OutlookWebServices -Identity administrator
In the Outlook 2007 computer, hold Ctrl key and click the outlook icon in system tray.
 select "Test E-mail AutoConfiguration..."
select "Test E-mail AutoConfiguration..."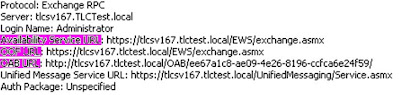 Availability Service URL: https://tlcsv167.tlctest.local/EWS/exchange.asmx
Availability Service URL: https://tlcsv167.tlctest.local/EWS/exchange.asmxOOF URL: https://tlcsv167.tlctest.local/EWS/exchange.asmx
OAB URL: https://tlcsv167.tlctest.local/OAB/ee67a1c8-ae09-4e26-8196-ccfa6e24f59/
==============
Free/Busy Publishing in Outlook
Outlook publishes free/busy data for a user periodically (by default every 15 minutes), and upon shutdown.
Tools-Options-Calendar Options—Free/Busy Options
 Click share your calendar ...
Click share your calendar ... Add national events to your calendar:
Add national events to your calendar:Tools--Options--Calendar Options --Click Add Holidays ... button
Deselect United State and Select Canada
Add BC Day to the Calendar:
click GO menu --Calendar --Action Menu
New All Day Events
Subject: BC Day

Tuesday, July 29, 2008
Exchange2007:Message Routing in a Coexistence Environment
Exchange 2003 organization

You should install the first Exchange 2007 server in VANCOUVER Site.
All Exchange 2007 servers belong to Exchange Routing Group (DWBGZMFD01QNBJR). When you install the first Exchange 2007 in VANCOUVER SITE, the routing group connector (two-way) between Exchange Routing Group (DWBGZMFD01QNBJR) and VANCOUVER routing group is created.
All messages that are relayed between Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2003 are routed through the initial routing group connector.

An Exchange 2007 is introduced into Burnaby Site. Tim's mailbox is hosted in Exchange 2003 of burnaby site. Chris's mailbox is hosted in Exchange 2007 of Burnaby Site.
When Tim sends mail to Chris, it will be routed through VANCOUVER Site and come back.
To avoid such excessive routing hops, you can create another routing group connector that connects the single Exchange 2007 routing group to the Burnaby routing group.
To avoid routing loop, modify the registry to suppress link state. Routing loop is a potential situation. It only occurs in a complex environment.
To suppress link state updates on Exchange 2003 or Exchange 2000
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\RESvc\Parameters.
Right-click Parameters and select New DWORD value. Name the new DWORD value SuppressStateChanges--value:1
Restart computer
New-RoutingGroupConnector -Name "RGC Burnaby Vancouver" -SourceTransportServers "Ex2007Burnaby.contoso.com" -TargetTransportServers "Ex2003Burnaby.contoso.com" -Cost 1 -bidirectional $true -PublicFolderReferralsEnabled $true

After a new routing group connector is created between Burnaby Routing Group and Exchange Routing Group, Tim sends mail directly to Chris without going through VANCOUVER SITE. However, if you want that message sent by Chris to TIM is routed without going through VANCOUVER SITE, you are better to assign the same cost for both routing group connectors.
The lowest cost routing path across routing group connectors is always used, and the Active Directory IP site link cost to reach the first routing group connector is only considered when two routing paths across routing group connectors have the same cost.
In the following diagram, all exchange 2007 servers are in same Exchange Routing Group, even though they are in different site.


Logical diagram of the routing groups communication:

Messages among Exchange 2007 servers are based on AD sites.
Messages from Exchange 2003 servers to Exchange 2007 and messages from Exchange 2007 to Exchange 2003 are based on Routing Group Connectors (RGC).
Example: A hub transport server in Site A delivers a message to Routing Group B.
Three possible routing paths exist.
Option 1:
RGC-1 and RGC 1-2 (10+10)
Option 2:
RGC-2 (10). The source mailbox is in Site A. Best routing path based on Routing Group Connector cost does not count the AD IP Site Link cost. The message travels from HUB Transport server in Site A to Hub Transport Server in Site B. Site B delivers the message to Routing Group B.
Option 3:
RGC-3 and RGC 2-3 (10+10)
The source mailbox is in Site A. Best routing path based on Routing Group Connector cost does not count the AD IP Site Link cost. The message travels from HUB Transport server in Site A to Hub Transport Server in Site C. Site C delivers the message to Routing Group C and then to Routing Group B.
Best route: option 2.
===
Routing loop
There are two reasons. If there are 2 or more connectors between two routing groups and primary connector is down, Exchange 2003 will pick the alternate connector (route). Exchange 2003 uses the minor link state method to notify each other about a down link. However, Exchange 2007 does not use the link state. Without knowing a routing group connector down, Exchange 2007 continues to route messages to the down connector.
Let me modify the cost of Routing Group Connectors.

Messages from Site A to routing group B.
Best route is RGC-3 (cost 5) + RGC 2-3 (cost 10).
However, RGC 2-3 is down. Because of the minor link state update, all Exchange 2003 servers know the RGC 2-3 down. However, Exchange 2007 servers don't have any knowledge of down link. Exchange 2007 servers still use the RGC-3 and RGC 2-3 route. When messages reach the Routing Group C, Routing Group C selects the RGC 1-3 path because the RGC 2-3 path down. When Routing Group A gets the messages, it routes them through RGC-1 connector because it has the lower cost.
Looping:









 ===============
===============